Minimal OpenGL example in C
03 Aug 2018OpenGL is a powerful cross-platform standard for 3D visualisation. OpenGL libraries use a domain specific language (shader language) to describe element-wise operations on vertices (vertex shader) and pixel values (fragment shader). More recent OpenGL versions also support geometry shaders and tesselation shaders (see OpenGL article on Wikipedia).
The learning curve for OpenGL is quite steep at the beginning. The reason is, that a program to draw a triangle is almost as complex as a program drawing thousands of triangles. It is also important to add code for retrieving error messages in order to be able to do development.
I haven’t found many minimal examples to understand OpenGL, so I am posting one here. The example draws a coloured triangle on the screen.
// Minimal OpenGL shader example using OpenGL directly
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <GL/glew.h>
#include <GL/glut.h>
const char *vertexSource = "#version 130\n\
in mediump vec3 point;\n\
in mediump vec2 texcoord;\n\
out mediump vec2 UV;\n\
void main()\n\
{\n\
gl_Position = vec4(point, 1);\n\
UV = texcoord;\n\
}";
const char *fragmentSource = "#version 130\n\
in mediump vec2 UV;\n\
out mediump vec3 fragColor;\n\
uniform sampler2D tex;\n\
void main()\n\
{\n\
fragColor = texture(tex, UV).rgb;\n\
}";
GLuint vao;
GLuint vbo;
GLuint idx;
GLuint tex;
GLuint program;
int width = 320;
int height = 240;
void onDisplay(void)
{
glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
glUseProgram(program);
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, 3, GL_UNSIGNED_INT, (void *)0);
glutSwapBuffers();
}
void onResize(int w, int h)
{
width = w; height = h;
glViewport(0, 0, (GLsizei)w, (GLsizei)h);
}
void printError(const char *context)
{
GLenum error = glGetError();
if (error != GL_NO_ERROR) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s: %s\n", context, gluErrorString(error));
};
}
void printStatus(const char *step, GLuint context, GLuint status)
{
GLint result = GL_FALSE;
if (status == GL_COMPILE_STATUS)
glGetShaderiv(context, status, &result);
else
glGetProgramiv(context, status, &result);
if (result == GL_FALSE) {
char buffer[1024];
if (status == GL_COMPILE_STATUS)
glGetShaderInfoLog(context, 1024, NULL, buffer);
else
glGetProgramInfoLog(context, 1024, NULL, buffer);
if (buffer[0])
fprintf(stderr, "%s: %s\n", step, buffer);
};
}
void printCompileStatus(const char *step, GLuint context)
{
printStatus(step, context, GL_COMPILE_STATUS);
}
void printLinkStatus(const char *step, GLuint context)
{
printStatus(step, context, GL_LINK_STATUS);
}
GLfloat vertices[] = {
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f
};
unsigned int indices[] = { 0, 1, 2 };
float pixels[] = {
0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f
};
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_RGB);
glutInitWindowSize(width, height);
glutCreateWindow("mini");
glewExperimental = GL_TRUE;
glewInit();
GLuint vertexShader = glCreateShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER);
glShaderSource(vertexShader, 1, &vertexSource, NULL);
glCompileShader(vertexShader);
printCompileStatus("Vertex shader", vertexShader);
GLuint fragmentShader = glCreateShader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER);
glShaderSource(fragmentShader, 1, &fragmentSource, NULL);
glCompileShader(fragmentShader);
printCompileStatus("Fragment shader", fragmentShader);
program = glCreateProgram();
glAttachShader(program, vertexShader);
glAttachShader(program, fragmentShader);
glLinkProgram(program);
printLinkStatus("Shader program", program);
glGenVertexArrays(1, &vao);
glBindVertexArray(vao);
glGenBuffers(1, &vbo);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vbo);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glGenBuffers(1, &idx);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, idx);
glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(indices), indices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glVertexAttribPointer(glGetAttribLocation(program, "point"), 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 5 * sizeof(float), (void *)0);
glVertexAttribPointer(glGetAttribLocation(program, "texcoord"), 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 5 * sizeof(float), (void *)(3 * sizeof(float)));
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
glUseProgram(program);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glGenTextures(1, &tex);
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, tex);
glUniform1i(glGetUniformLocation(program, "tex"), 0);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB, 2, 2, 0, GL_BGR, GL_FLOAT, pixels);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
glutDisplayFunc(onDisplay);
glutReshapeFunc(onResize);
glutMainLoop();
glDisableVertexAttribArray(1);
glDisableVertexAttribArray(0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0);
glDeleteTextures(1, &tex);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &idx);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &vbo);
glBindVertexArray(0);
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &vao);
glDetachShader(program, vertexShader);
glDetachShader(program, fragmentShader);
glDeleteProgram(program);
glDeleteShader(vertexShader);
glDeleteShader(fragmentShader);
return 0;
}The example uses the widely supported OpenGL version 3.1 (which has the version tag 130). You can download, compile, and run the example as follows:
wget https://www.wedesoft.de/downloads/raw-opengl.c
gcc -o raw-opengl raw-opengl.c -lGL -lGLEW -lGLU -lglut
./raw-opengl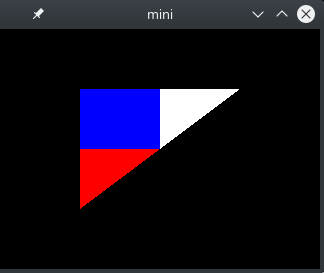
Any feedback, comments, and suggestions are welcome.
Enjoy!